GlyCulator 2.0
The most important while using GlyCulator2 is: the program requires files analyzed to be formatted in a uniform way. Since a user is asked to provide some information about the files, the pieces of information need to hold true for all files provided. If a user wants to analyze two types of files, I recommend to prepare two batches of files and analyze them with GlyCulator2 seperately.
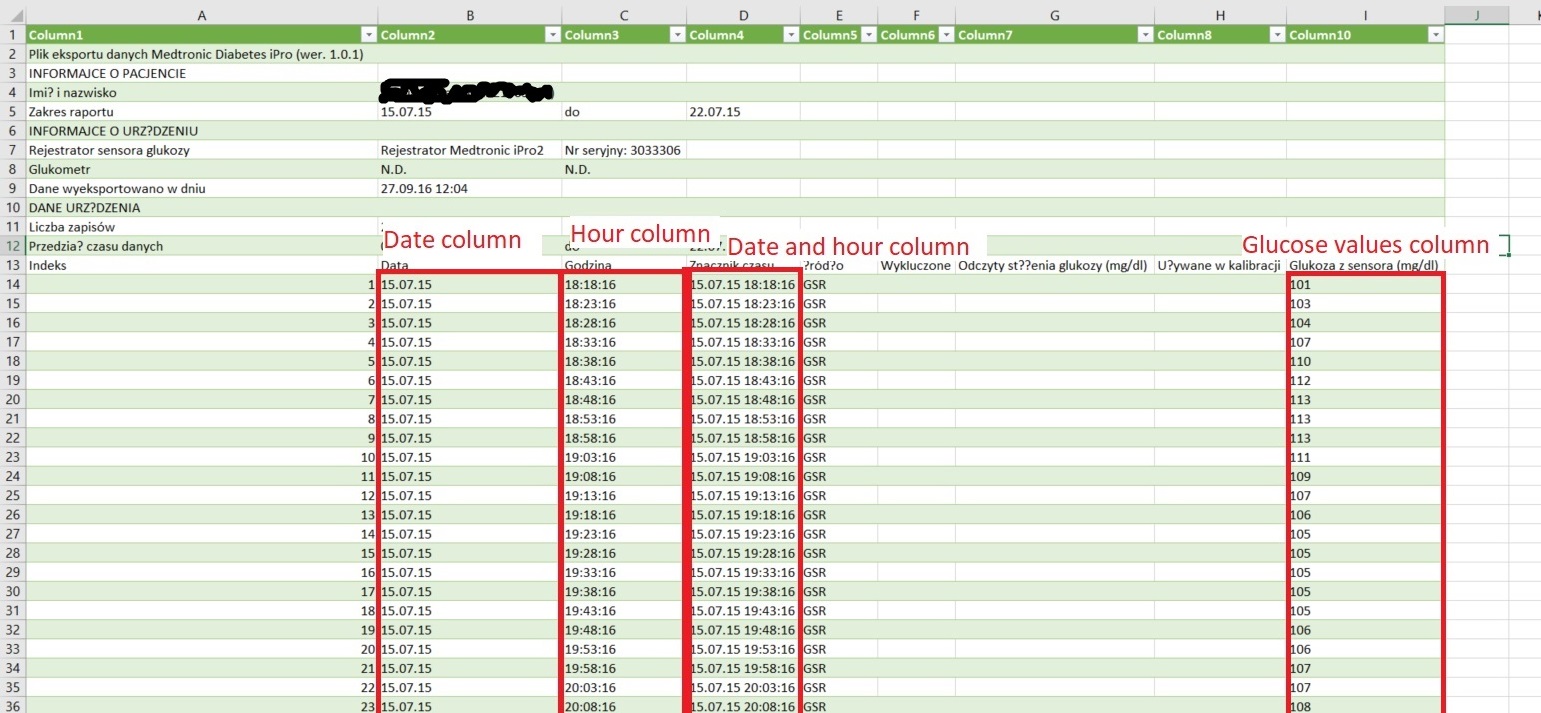
Glyculator2 requires user to submit: (please note that the numbering of columns and rows begins from 1)
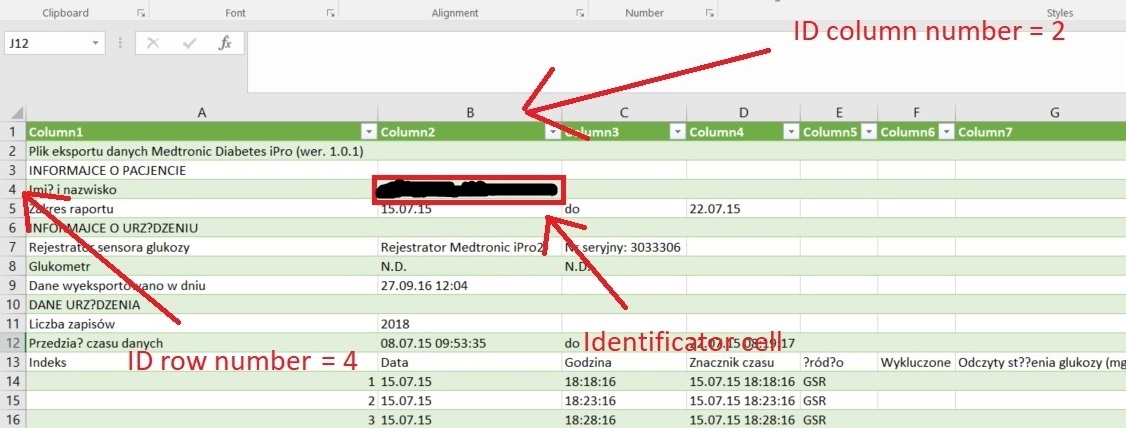
- column number and row number of a cell which contains a name or identification of each file (must be the same in all files)
- number of time points per day - which is related to the interval of the recordings. Please input 288, if the interval is 5 minutes
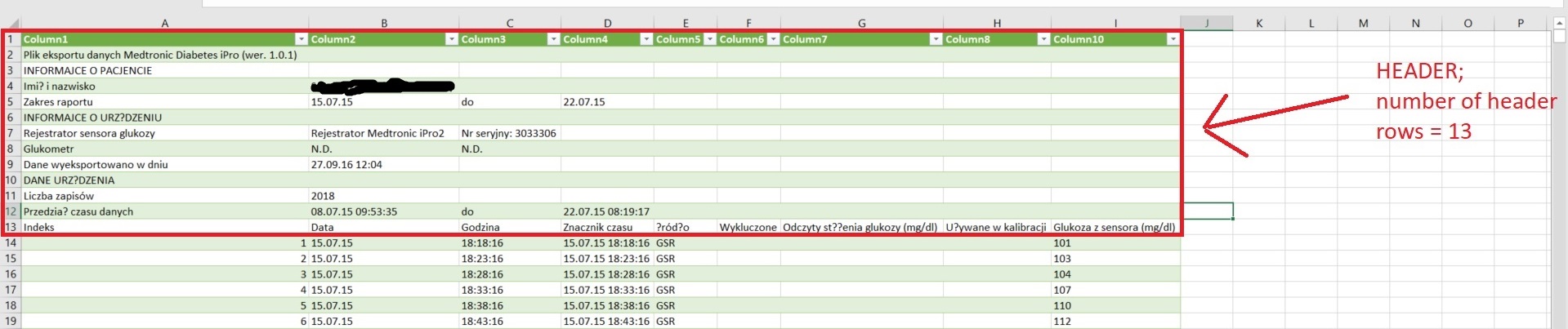
- number of header rows in all files - this an optional argument. If your files do not contain headers, change it to 0
- you have to specify either the numbers of columns with dates and hours or the number of a column which contains the full date. If your files contain no column with date and hour, please leave the field blank. If your files do not have two seperate columns with dates and numbers, you can leave the appropriate fields empty or leave them as they are. GlyCulator2 will take only the column with date and hour to consideration
- column number with glucose values
- format of the date: please specify the order of day, month, year as well as hours, minutes and optionally seconds. E.g.: mdy_hm for a format like this: 9/27/99 13:13; ymd_hms for a format like this: 17.10.21 13:41:59. The seperator can be: :, ., /
- provide file extension of your files. Currently supported are: .csv, .txt, .xlsx, .xls
- if your files are in a .csv format, please provide a character which fulfills the seperator role in your files
- files to analyze. You can choose any files from you PC, by clicking the <Browse> button.
To better illustrate what is what in a CGM file, following images of a raw CGM data file are marked with names of input fields.
Further instructions and explanations can be found in a manual document. Click here to download manual.
GlyCulator2 was created by Konrad Pagacz to calculate glycaemic variability indices from raw continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) or flash glucose monitoring (FGM) data. It accepts raw CGM or FGM files in .xls, .xlsx, .csv, .txt formats and calculates the following glycaemic variability indices:
- mean
- standard deviation (SD)
- median, coefficient of variation (CV), M100 index
- low/high blood glucose index
- estimated HbA1c
- J-index
- mean amplitude of glycaemic excursion (MAGE)
- mean of daily differences (MODD)
- continuous overall net glycaemic action (CONGA)
- percent of measurements below 70 mg/dl (3.9 mmol)
- percent of measurements over 180 mg/dl (10 mmol/l)
- glycaemic risk assessment in diabetes equation (GRADE) and GRADE's appropriate percentages.
The tool follows guidelines on CGM reporting specified in the International Consensus on Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring.
M100, J-index were calculated using formulas provided by F. John Service in: Service, F. J. (2013). Glucose Variability. Diabetes, 62(5), 1398–1404. http://doi.org/10.2337/db12-1396.
MAGE algorithm was adapted from: Baghurst, P. A. (2011). Calculating the mean amplitude of glycemic excursion from continuous glucose monitoring data: an automated algorithm. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics, 13(3), 296–302. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2010.0090.
MODD and CONGA algorithms were implemented after: McDonnell, C. M., Donath, S. M., Vidmar, S. I., Werther, G. a, & Cameron, F. J. (2005). A novel approach to continuous glucose analysis utilizing glycemic variation. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics, 7(2), 253–63. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2005.7.253.
GRADE calculations follow: Hill, N. R., Hindmarsh, P. C., Stevens, R. J., Stratton, I. M., Levy, J. C., & Matthews, D. R. (2007). A method for assessing quality of control from glucose profiles. Diabetic Medicine : A Journal of the British Diabetic Association, 24(7), 753–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2007.02119.x.
Further instructions and explanations can be found in a manual document. Click here to download manual.
Click here to download the old version of GlyCulator - GlyCulator1.
This software is a part of paper entitled 'GlyCulator2: an update on a web application for calculation of glycemic variability indices' and authored by Konrad Pagacz, Konrad Stawiski, Agnieszka Szadkowska, Wojciech Mlynarski, Wojciech Fendler.
Click here to download old version of GlyCulator - GlyCulator 1.0.
| © Version 2.0 revision 68 (bb052c4f3297dc076dfdf0294de52c264ce4df73) Software author, technical issues: Konrad Pagacz, MD (contact: konrad.pagacz@umed.lodz.pl; Department of Biostatistics and Translational Medicine, Medical University of Lodz, Poland) |  |